Things to Know About Open Wound CareThings to Know About Open Wound Care
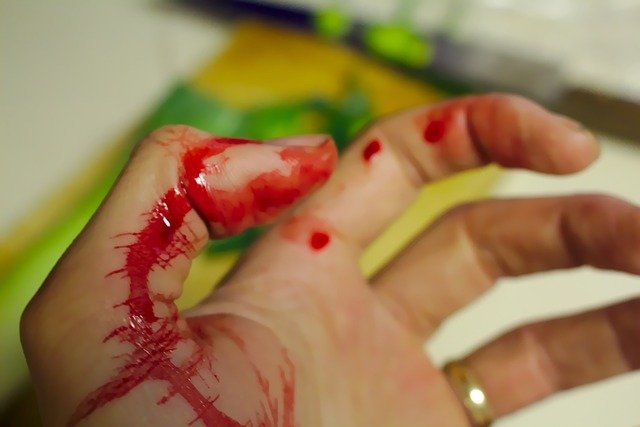
An open wound involves an external or internal break in body tissue, usually involving the skin. Nearly everyone will experience open wound at some point in their life. Most open wounds are minor and can be treated at home. Falls, accidents with sharp objects, and car accidents are the most common causes of open injuries. In the case of a severe accident, you should seek immediate medical care, and usually, it requires an assessment as cited by https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-68195-5_80. This post will cover types of open wounds and how to treat them in more detail below.
Types
Depending on their cause, there are five types of open wounds, which are classified below.
Abrasion. An abrasion occurs when the skin is rubbed or slipped on a rugged surface. Although abrasions produce little blood, it is essential to disinfect the wound and remove all debris to prevent disease.
Laceration. A laceration is a deep opening or tears in the skin. Cuts are usually caused by accidents or accidents with machines, knives, or other sharp instruments. This type of wound can cause significant bleeding.
Avulsion. With an avulsion, the skin and underlying tissue gradually tear by force. Avulsions are caused by violent episodes such as explosions, animal attacks, or car accidents.
Puncture. A puncture wound is a small hole in soft tissue. Splinters and needles can cause serious puncture wounds that only affect the outer layers of tissue. However, knife or bullet wounds can damage deep muscles and internal organs, which can cause bleeding.
Incision. Incisions are used in many surgical procedures. Incisions often cause significant and rapid bleeding. Deep incisions can damage muscles or nerves and will most likely require incisions.
Treatments
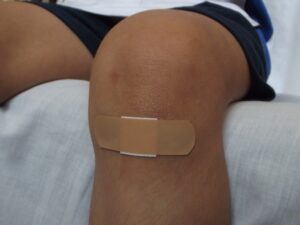 Minor or even acute open wounds may not require medical attention. People can treat these wounds at home. However, acute open injuries involving significant bleeding may require immediate medical attention. First, you should stop the bleeding by applying pressure to the wound via bandages or a clean cloth to promote blood circulation. Then clean the injury as soon as possible with water and saline solution to flush away any debris and apply a thin layer of antibiotic ointment to prevent infection. Next, close and dress the wound with bandages.
Minor or even acute open wounds may not require medical attention. People can treat these wounds at home. However, acute open injuries involving significant bleeding may require immediate medical attention. First, you should stop the bleeding by applying pressure to the wound via bandages or a clean cloth to promote blood circulation. Then clean the injury as soon as possible with water and saline solution to flush away any debris and apply a thin layer of antibiotic ointment to prevent infection. Next, close and dress the wound with bandages.
Washing the wound closure aids promotes faster wound healing. Deep, open wounds may require sutures or staples. However, leave an already infected wound accessible before the disease subsides. Soiled dressings must be removed and checked every 24 hours for signs of infection.
Medications for Open Wounds
People can take over-the-counter painkillers to reduce inflammation and painful symptoms during the healing process. However, please stay away from aspirin because it can cause swelling and wait for the wound to heal. A healthcare professional may prescribe stronger pain medications for people with severe or infected injuries. For minor cuts and abrasions, topical creams may be used. A health care professional may prescribe oral antibiotics if they think a person is more likely to develop a disorder during healing.